
February 23, 2024 | By Anonymous Source
Electrocardiograms (EKG or ECG) and telemetry are indispensable tools in the field of cardiac health. They have revolutionized how healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor various heart conditions, from arrhythmias to heart attacks. EKGs record the heart’s electrical activity, while telemetry involves wireless data transmission from a patient’s heart to a healthcare provider.
By providing real-time data on heart rate, rhythm, and other important parameters, EKG and telemetry enable doctors to detect and diagnose any abnormalities in heart function quickly. This information is crucial in determining the best course of treatment for patients, whether medication, surgery, or other interventions.
Moreover, EKG and telemetry also play a vital role in preventive healthcare. By gaining a deeper understanding of their heart health through these technologies, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy heart. This includes lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
This article aims to simplify the concepts of EKG and telemetry for better understanding, especially for those who review documentation. While it is the responsibility of a physician to analyze and interpret patient interactions and diagnostic tests, knowing about EKG and telemetry can be very useful for coders, auditors, and compliance professionals who work with physicians to improve documentation.
An electrocardiogram (EKG) is a visual representation of the electrical activity that occurs in the heart. This test measures and records the electrical signals generated by the heart and presents them as a series of waves and intervals on a graph. The purpose of an EKG is to help healthcare professionals interpret the heart’s electrical activity and detect any irregularities or abnormalities that may exist.
The EKG graph comprises P, QRS, and T waves and intervals.
- P Wave: The P wave represents the electrical signal that triggers the atria’s contraction (the heart’s top chambers).
- QRS Complex: The QRS complex represents the electrical signal that triggers the contraction of the ventricles (the bottom chambers of the heart).
- T Wave: The T wave represents the electrical signal associated with the recovery or relaxation of the ventricles.
The intervals on the ECG graph provide specific information about the timing of the electrical impulses that regulate the heart’s contractions. The PR interval measures the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles, represented by the interval between the P wave and the QRS complex. The QT interval measures the total time it takes for the ventricles to contract and recover, which includes the time for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. These intervals are essential in diagnosing and monitoring patients with heart conditions such as arrhythmias.

You can calculate your heart rate by counting the number of R waves in a 6-second strip and multiplying by 10. This will give you the beats per minute (BPM).
Telemetry is a medical process that involves using a device to monitor and record the electrical activity of the heart. The device, a telemetry unit, is connected to the patient and continuously records and transmits data on the heart’s electrical activity to a monitoring station. This monitoring method is often used in hospitals for patients requiring constant cardiac monitoring, such as those recently undergoing heart surgery. It can also be used for at-home monitoring of patients with cardiac conditions. Interpreting telemetry requires analyzing the data transmitted by the device, including heart rate, rhythm, and any abnormalities, and comparing it to the patient’s medical history and current condition. This allows doctors and medical professionals to monitor patients closely and make informed decisions about their care.
When the heart is beating normally, the pattern on the telemetry display is regular and consistent. The heart rate falls within a typical range, usually between 60 to 100 BPM at rest.
Telemetry can quickly detect abnormal heart rhythms, such as arrhythmias. Some common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation (irregular, rapid heartbeat) and bradycardia (slow heart rate). When these occur, the waveform on the monitor may be irregular or absent. 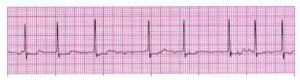
Telemetry systems have alarms that alert healthcare professionals to significant changes in your heart rhythm. They can quickly respond to any issues, ensuring your safety.
Conclusion
EKGs record the electrical activity of your heart at a specific moment, while telemetry offers continuous monitoring, making it ideal for detecting abnormal rhythms. Both require physician interpretation and documentation in the medical record. How each is documented will impact how the MDM of the E/M service is analyzed.








